Applying Image Masks to a Layer
Another way you can create transparency in a layer is by using image masks. An image mask creates transparency in a layer by deriving an alpha channel from another layer, such as a shape, text, movie, or still image.

Note: You can use masks and image masks together.
The power of image masks is that they do not have to be drawn or animated. Instead, you can use virtually any image or movie clip to create transparency in another layer. By default, movie clips create animated image masks, but you can also set an image mask to use only a single frame.
Image masks can also be used to assign masks created in other applications. For example, you can import an animated mask that was created in another application and exported as a QuickTime movie into your Motion project, then use it as an image mask.
When you use a layer as an image mask, you can choose which of the layer’s channels to apply to create transparency via the Source Channel pop-up menu in the Image Mask Inspector. The choices include:
Red
Green
Blue
Alpha
Luminance
Because alpha channels are basically 8-bit grayscale images, you can use any single color channel as an image mask. You can also use another layer’s alpha channel. Luminance allows you to use the aggregate luminance from the red, green, and blue channels of an image to create transparency. For all these options, color is ignored.
Assigning an image mask is a two-part process. First, you create a blank image mask underneath a layer. Then you assign the image you want to use to create transparency.
Select the layer to mask.
Choose Object > Add Image Mask (or press Command-Shift-M).
The image mask appears underneath the layer in the Layers list and Timeline.
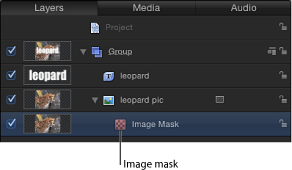
With the image mask selected, do one of the following:
Open the Image Mask Inspector, then drag the layer to use as the mask into the Mask Source well.
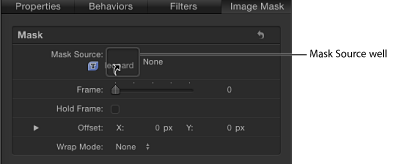
Drag the layer to use as the mask into the Mask Source well in the HUD.
Important: Click and drag in one movement to successfully drop a layer in an image well. If you select the layer to use as the source, then release the mouse button, you lose the selection.
In this example, text is used as the mask layer.
Choose the channel you want to use to create transparency from the Source Channel pop-up menu, as well as any other options necessary to create the required transparency.

Applying Filters to Image Masks
Like shape masks, you can add filters to image masks to further manipulate the transparency effect. You may be able to improve the mask that’s created by using color correction filters such as Brightness, Contrast, and Gamma to manipulate the contrast of the mask, pulling out or reducing detail to create the transparency effect you need.
Filtering image masks works identically to filtering shape masks. For more information, see Applying Filters to Masks.
Applying Behaviors to Image Masks
You can also apply behaviors to image masks to create animated transparency effects. For more information, see Applying Behaviors to Masks.