Setting Environment Variables in Apple Qmaster
You may want to set or change an environment variable for submitting certain jobs. When you set an environment variable within Apple Qmaster, the new setting takes effect immediately. This gives you an easy way to do things such as setting common directory paths or plug-in-specific environment variables for Apple Qmaster jobs.
To set environment variables in Apple Qmaster
Select the command for which you want to set an environment variable.
Click the Set Environment button.
In the dialog that appears, you can add preflight scripts and environment variables or edit or remove an existing one.
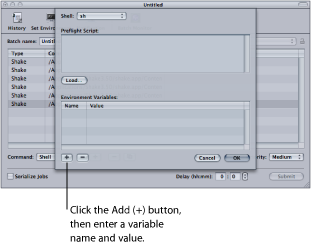
- To add a variable: Click the Add (+) button, then select and edit Untitled Variable in both the Name and Value columns.
- To remove a variable: Select it, then click the Remove (–) button.
Click OK.
Your environment variables take effect immediately, and are retained only for the selected command.